4.20. RMM-EL3 Communication interface
This document defines the communication interface between RMM and EL3. There are two parts in this interface: the boot interface and the runtime interface.
The Boot Interface defines the ABI between EL3 and RMM when the CPU enters R-EL2 for the first time after boot. The cold boot interface defines the ABI for the cold boot path and the warm boot interface defines the same for the warm path.
The RMM-EL3 runtime interface defines the ABI for EL3 services which can be invoked by RMM as well as the register save-restore convention when handling an SMC call from NS.
The below sections discuss these interfaces more in detail.
4.20.1. RMM-EL3 Interface versioning
The RMM Boot and Runtime Interface uses a version number to check compatibility with the register arguments passed as part of Boot Interface and RMM-EL3 runtime interface.
The Boot Manifest, discussed later in section Boot Manifest, uses a separate version number but with the same scheme.
The version number is a 32-bit type with the following fields:
Bits |
Value |
|---|---|
[0:15] |
|
[16:30] |
|
[31] |
RES0 |
The version numbers are sequentially increased and the rules for updating them are explained below:
VERSION_MAJOR: This value is increased when changes break compatibility with previous versions. If the changes on the ABI are compatible with the previous one,VERSION_MAJORremains unchanged.
VERSION_MINOR: This value is increased on any change that is backwards compatible with the previous version. WhenVERSION_MAJORis increased,VERSION_MINORmust be set to 0.
RES0: Bit 31 of the version number is reserved 0 as to maintain consistency with the versioning schemes used in other parts of RMM.
This document specifies the 0.8 version of Boot Interface ABI and RMM-EL3 services specification and the 0.5 version of the Boot Manifest.
4.20.2. RMM Boot Interface
This section deals with the Boot Interface part of the specification.
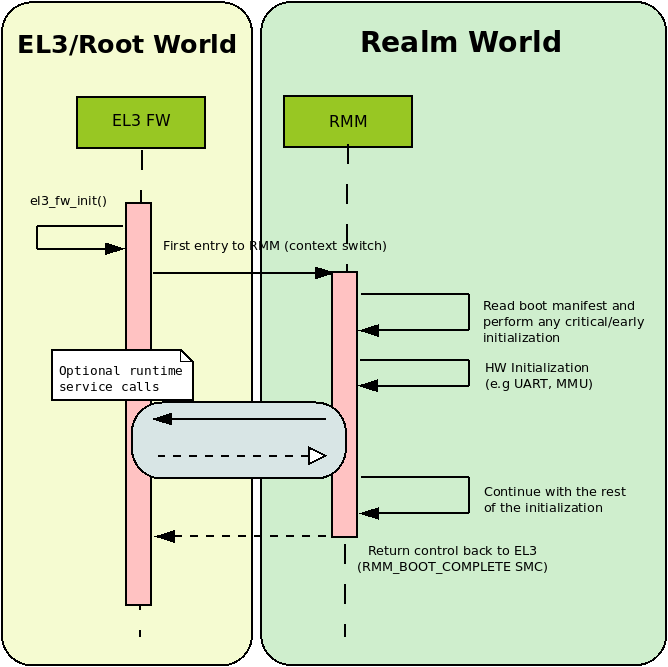
One of the goals of the Boot Interface is to allow EL3 firmware to pass down into RMM certain platform specific information dynamically. This allows RMM to be less platform dependent and be more generic across platform variations. It also allows RMM to be decoupled from the other boot loader images in the boot sequence and remain agnostic of any particular format used for configuration files.
The Boot Interface ABI defines a set of register conventions and also a memory based manifest file to pass information from EL3 to RMM. The Boot Manifest and the associated platform data in it can be dynamically created by EL3 and there is no restriction on how the data can be obtained (e.g by DTB, hoblist or other).
The register convention and the manifest are versioned separately to manage future enhancements and compatibility.
RMM completes the boot by issuing the RMM_BOOT_COMPLETE SMC (0xC40001CF)
back to EL3. After the RMM has finished the boot process, it can only be
entered from EL3 as part of RMI handling.
If RMM returns an error during boot (in any CPU), then RMM must not be entered from any CPU.
4.20.2.1. Cold Boot Interface
During cold boot RMM expects the following register values:
Register |
Value |
|---|---|
x0 |
Linear index of this PE. This index starts from 0 and must be less than the maximum number of CPUs to be supported at runtime (see x2). |
x1 |
Version for this Boot Interface as defined in RMM-EL3 Interface versioning. |
x2 |
Maximum number of CPUs to be supported at runtime. RMM should ensure that it can support this maximum number. |
x3 |
Base address for the shared buffer used for communication between EL3 firmware and RMM. This buffer must be of 4KB size (1 page). The Boot Manifest must be present at the base of this shared buffer during cold boot. |
x4 |
Activation token. Should be set to 0 on the initial boot of the system. For a subsequent warm boot or when using Live Firmware Activation, the activation token should be set to the value returned by RMM for this CPU during the initial boot (in x2). |
During cold boot, EL3 firmware needs to allocate a 4KB page that will be passed to RMM in x3. This memory will be used as shared buffer for communication between EL3 and RMM. It must be assigned to Realm world and must be mapped with Normal memory attributes (IWB-OWB-ISH) at EL3. At boot, this memory will be used to populate the Boot Manifest. Since the Boot Manifest can be accessed by RMM prior to enabling its MMU, EL3 must ensure that proper cache maintenance operations are performed after the Boot Manifest is populated.
EL3 should also ensure that this shared buffer is always available for use by RMM during the lifetime of the system and that it can be used for runtime communication between RMM and EL3. For example, when RMM invokes attestation service commands in EL3, this buffer can be used to exchange data between RMM and EL3. It is also allowed for RMM to invoke runtime services provided by EL3 utilizing this buffer during the boot phase, prior to return back to EL3 via RMM_BOOT_COMPLETE SMC.
RMM should map this memory page into its Stage 1 page-tables using Normal memory attributes.
During runtime, it is the RMM which initiates any communication with EL3. If that communication requires the use of the shared area, it is expected that RMM needs to do the necessary concurrency protection to prevent the use of the same buffer by other PEs.
The following sequence diagram shows how a generic EL3 Firmware would boot RMM.
4.20.2.2. Warm Boot Interface
At warm boot, RMM is already initialized and only some per-CPU initialization is still pending. The only argument that is required by RMM at this stage is the CPU Id, which will be passed through register x0 whilst x1 to x3 are RES0. This is summarized in the following table:
Register |
Value |
|---|---|
x0 |
Linear index of this PE. This index starts from 0 and must be less than the maximum number of CPUs to be supported at runtime (see x2). |
x1 |
Activation token. Should be set to 0 on the initial boot of the system. For a subsequent warm boot or when using Live Firmware Activation, the activation token should be set to the value returned by RMM for this CPU during the initial boot (in x2). |
x2 - x3 |
RES0 |
4.20.2.3. Boot error handling and return values
After boot up and initialization, RMM returns control back to EL3 through a
RMM_BOOT_COMPLETE SMC call. The first argument of this SMC call will
be returned in x1 and it will encode a signed integer with the error reason.
x2 will contain the per-CPU activation token, which is an opaque value that
should be passed back to RMM when doing Live Firmware Activations or on a
subsequent warm boot.
The following table describes possible values for the error code in x1:
Error code |
Description |
ID |
|---|---|---|
|
Boot successful |
0 |
|
Unknown error |
-1 |
|
Boot Interface version reported by EL3 is not supported by RMM |
-2 |
|
Number of CPUs reported by EL3 larger than maximum supported by RMM |
-3 |
|
Current CPU Id is higher or equal than the number of CPUs supported by RMM |
-4 |
|
Invalid pointer to shared memory area |
-5 |
|
Version reported by the Boot Manifest not supported by RMM |
-6 |
|
Error parsing core Boot Manifest |
-7 |
For any error detected in RMM during cold or warm boot, RMM will return back to
EL3 using RMM_BOOT_COMPLETE SMC with an appropriate error code. It is
expected that EL3 will take necessary action to disable Realm world for further
entry from NS Host on receiving an error. This will be done across all the PEs
in the system so as to present a symmetric view to the NS Host. Any further
warm boot by any PE should not enter RMM using the warm boot interface.
4.20.2.4. Boot Manifest
During cold boot, EL3 Firmware passes a memory Boot Manifest to RMM containing platform information.
This Boot Manifest is versioned independently of the Boot Interface, to help
evolve the former independent of the latter.
The current version for the Boot Manifest is v0.4 and the rules explained
in RMM-EL3 Interface versioning apply on this version as well.
The Boot Manifest v0.4 has the following fields:
version : Version of the Manifest (v0.4)
plat_data : Pointer to the platform specific data and not specified by this document. These data are optional and can be NULL.
plat_dram : Structure encoding the NS DRAM information on the platform. This field is optional and platform can choose to zero out this structure if RMM does not need EL3 to send this information during the boot.
plat_console : Structure encoding the list of consoles for RMM use on the platform. This field is optional and platform can choose to not populate the console list if this is not needed by the RMM for this platform.
For the current version of the Boot Manifest, the core manifest contains a pointer to the platform data. EL3 must ensure that the whole Boot Manifest, including the platform data, if available, fits inside the RMM EL3 shared buffer.
For the data structure specification of Boot Manifest, refer to RMM-EL3 Boot Manifest structure
4.20.3. RMM-EL3 Runtime Interface
This section defines the RMM-EL3 runtime interface which specifies the ABI for EL3 services expected by RMM at runtime as well as the register save and restore convention between EL3 and RMM as part of RMI call handling. It is important to note that RMM is allowed to invoke EL3-RMM runtime interface services during the boot phase as well. The EL3 runtime service handling must not result in a world switch to another world unless specified. Both the RMM and EL3 are allowed to make suitable optimizations based on this assumption.
If the interface requires the use of memory, then the memory references should be within the shared buffer communicated as part of the boot interface. See Cold Boot Interface for properties of this shared buffer which both EL3 and RMM must adhere to.
4.20.3.1. RMM-EL3 runtime service return codes
The return codes from EL3 to RMM is a 32 bit signed integer which encapsulates error condition as described in the following table:
Error code |
Description |
ID |
|---|---|---|
|
No errors detected |
0 |
|
Unknown/Generic error |
-1 |
|
The value of an address used as argument was invalid |
-2 |
|
Incorrect PAS |
-3 |
|
Not enough memory to perform an operation |
-4 |
|
The value of an argument was invalid |
-5 |
|
The resource is busy. Try again. |
-6 |
If multiple failure conditions are detected in an RMM to EL3 command, then EL3 is allowed to return an error code corresponding to any of the failure conditions.
4.20.3.2. RMM-EL3 runtime services
The following table summarizes the RMM runtime services that need to be implemented by EL3 Firmware.
FID |
Command |
|---|---|
0xC400018F |
|
0xC40001B0 |
|
0xC40001B1 |
|
0xC40001B2 |
|
0xC40001B3 |
|
0xC40001B4 |
|
0xC40001B5 |
|
0xC40001B6 |
|
0xC40001B7 |
|
0xC40001B8 |
|
0xC40001B9 |
|
0xC40001BA |
|
0xC40001BB |
|
4.20.3.2.1. RMM_RMI_REQ_COMPLETE command
Notifies the completion of an RMI call to the Non-Secure world.
This call is the only function currently in RMM-EL3 runtime interface which results in a world switch to NS. This call is the reply to the original RMI call and it is forwarded by EL3 to the NS world.
4.20.3.2.1.1. FID
0xC400018F
4.20.3.2.1.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
err_code |
x1 |
[63:0] |
RmiCommandReturnCode |
Error code returned by the RMI service invoked by NS World. See Realm Management Monitor specification for more info |
4.20.3.2.1.3. Output values
This call does not return.
4.20.3.2.1.4. Failure conditions
Since this call does not return to RMM, there is no failure condition which can be notified back to RMM.
4.20.3.2.2. RMM_GTSI_DELEGATE command
Delegate a memory granule by changing its PAS from Non-Secure to Realm.
4.20.3.2.2.1. FID
0xC40001B0
4.20.3.2.2.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
base_pa |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Address |
PA of the start of the granule to be delegated |
4.20.3.2.2.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
4.20.3.2.2.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The granule pointed by |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.3.2.3. RMM_GTSI_UNDELEGATE command
Undelegate a memory granule by changing its PAS from Realm to Non-Secure.
4.20.3.2.3.1. FID
0xC40001B1
4.20.3.2.3.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
base_pa |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Address |
PA of the start of the granule to be undelegated |
4.20.3.2.3.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
4.20.3.2.3.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
|
|
The granule pointed by |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.3.2.4. RMM_ATTEST_GET_REALM_KEY command
Retrieve the Realm Attestation Token Signing key from EL3.
4.20.3.2.4.1. FID
0xC40001B2
4.20.3.2.4.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
buf_pa |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Address |
PA where the Realm Attestation Key must be stored by EL3. The PA must belong to the shared buffer |
buf_size |
x2 |
[63:0] |
Size |
Size in bytes of the Realm Attestation Key buffer. |
ecc_curve |
x3 |
[63:0] |
Enum |
Type of the elliptic curve to which the requested attestation key belongs to. See Supported ECC Curves |
4.20.3.2.4.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
keySize |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Size |
Size of the Realm Attestation Key |
4.20.3.2.4.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An unknown error occurred whilst processing the command |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.3.2.4.5. Supported ECC Curves
ID |
Curve |
|---|---|
0 |
ECC SECP384R1 |
4.20.3.2.5. RMM_ATTEST_GET_PLAT_TOKEN command
Retrieve the Platform Token from EL3. If the entire token does not fit in the
buffer, EL3 returns a hunk of the token (via tokenHunkSize parameter) and
indicates the remaining bytes that are pending retrieval (via remainingSize
parameter). The challenge object for the platform token must be populated in
the buffer for the first call of this command and the size of the object is
indicated by c_size parameter. Subsequent calls to retrieve remaining hunks of
the token must be made with c_size as 0.
If c_size is not 0, this command could cause regeneration of platform token
and will return token hunk corresponding to beginning of the token.
It is valid for the calls of this command to return E_RMM_AGAIN error,
which is an indication to the caller to retry this command again. Depending on the
platform, this mechanism can be used to implement queuing to HES, if HES is
involved in platform token generation.
4.20.3.2.5.1. FID
0xC40001B3
4.20.3.2.5.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
buf_pa |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Address |
PA of the platform attestation token. The challenge object must be passed in this buffer for the first call of this command. Any subsequent calls, if required to retrieve the full token, should not have this object. The PA must belong to the shared buffer. |
buf_size |
x2 |
[63:0] |
Size |
Size in bytes of the platform attestation token buffer. |
c_size |
x3 |
[63:0] |
Size |
Size in bytes of the challenge object. It corresponds to the size of one of the defined SHA algorithms. Any subsequent calls, if required to retrieve the full token, should set this size to 0. |
4.20.3.2.5.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
tokenHunkSize |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Size |
Size of the platform token hunk retrieved |
remainingSize |
x2 |
[63:0] |
Size |
Remaining bytes of the token that are pending retrieval |
4.20.3.2.5.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
Resource for Platform token retrieval is busy. Try again. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
An unknown error occurred whilst processing the command |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.3.2.6. RMM_EL3_FEATURES command
This command provides a mechanism to discover features and ABIs supported by the RMM-EL3 interface, for a given version. This command is helpful when there are platform specific optional RMM-EL3 interfaces and features exposed by vendor specific EL3 firmware, and a generic RMM that can modify its behavior based on discovery of EL3 features.
The features can be discovered by specifying the feature register index that
has fields defined to indicate presence or absence of features and other
relevant information. The feature register index is specified in the
feat_reg_idx parameter. Each feature register is a 64 bit register.
This command is available from v0.4 of the RMM-EL3 interface.
The following is the register definition for feature register index 0 for v0.4 of the interface:
4.20.3.2.6.1. RMM-EL3 Feature Resister 0
63 32 31 16 15 8 7 1 0
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+
^
|
RMMD_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN
Bit Fields:
- Bit 0: RMMD_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN
When set to 1, the RMMD_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN feature is enabled.
When cleared (0), the feature is disabled.
Bits [1:63]: Reserved (must be zero)
4.20.3.2.6.2. FID
0xC40001B4
4.20.3.2.6.3. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
feat_reg_idx |
x1 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Feature register index. For v0.4, a value of 0 is the only acceptable value |
4.20.3.2.6.4. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
feat_reg |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Value |
Value of the register as defined above |
4.20.3.2.6.5. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
|
|
if the SMC is not present, if interface version is <0.4 |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.3.2.7. RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN command
This command is an optional command that can be discovered using the RMM_EL3_FEATURES command. This command is used to send requests related to realm attestation token signing requests to EL3. The command supports 3 opcodes:
RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_PUSH_REQ_OP
RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_PULL_RESP_OP
RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_GET_RAK_PUB_OP
The above opcodes can be used to send realm attestation token signing requests to EL3 and get their response, so that the realm attestation token can be constructed.
This command is useful when the RMM may not have access to the private portion of the realm attestation key and needs signing services from EL3 or CCA HES, or other platform specific mechanisms to perform signing.
The RMM-EL3 interface for this command is modeled as two separate queues, one for signing requests and one for retrieving the signed responses. It is possible that the queue in EL3 is full or EL3 is busy and unable to service the RMM requests, in which case the RMM is expected to retry the push operation for requests and pop operation for responses.
4.20.3.2.7.1. FID
0xC40001B5
4.20.3.2.7.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
opcode |
x1 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Opcode that is one of:
|
buf_pa |
x2 |
[63:0] |
Address |
PA where the request structure is stored for the opcode RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_PUSH_REQ_OP, the response structure needs to be populated for the opcode RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_PULL_RESP_OP, or where the public key must be populated for the opcode RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_GET_RAK_PUB_OP. The PA must belong to the RMM-EL3 shared buffer |
buf_size |
x3 |
[63:0] |
Size |
Size in bytes of the input buffer in |
ecc_curve |
x4 |
[63:0] |
Enum |
Type of the elliptic curve to which the requested attestation key belongs to. See Supported ECC Curves. This parameter is valid on for the opcode RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_GET_RAK_PUB_OP |
4.20.3.2.7.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status. Valid for all opcodes listed in input values |
retval1 |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Value |
If opcode is RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_GET_RAK_PUB_OP, then returns length of public key returned. Otherwise, reserved |
4.20.3.2.7.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
if opcode is invalid or buffer address and length passed to the EL3 are not in valid range corresponding to the RMM-EL3 shared buffer, or if the curve used for opcode RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_GET_RAK_PUB_OP is not the ECC P384 curve |
|
if the SMC is not present, if interface version is <0.4 |
|
For opcode RMM_EL3_TOKEN_SIGN_PUSH_REQ_OP, if the request is not queued since the EL3 queue is full, or if the response is not ready yet, for other opcodes |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.3.2.8. RMM_MEC_REFRESH command
This command updates the tweak for the encryption key/programs a new encryption key associated with a given MECID. After the execution of this command, all memory accesses associated with the MECID are encrypted/decrypted using the new key. This command is available from v0.8 of the RMM-EL3 interface.
4.20.3.2.8.1. FID
0xC40001B6
4.20.3.2.8.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
mecid |
x1 |
[47:32] |
UInt64 |
mecid is a 16-bit value between 0 and 65,535 that identifies the MECID for which the encryption key is to be updated. Value has to be a valid MECID as per field MECIDWidthm1 read from MECIDR_EL2. Bits [63:16] must be 0. |
mecid |
x1 |
[31:1] |
UInt64 |
Reserved, MBZ |
reason |
x1 |
[0] |
UInt64 |
reason is a single bit field used to indicate the reason for the MEC refresh. Values are: 0 (Realm creation), 1 (Realm destruction). |
4.20.3.2.8.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status. Valid for all opcodes listed in input values |
4.20.3.2.8.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
If a field in the x1 register is incorrectly encoded or if MECID is invalid (larger than the common MECID width, determined by MECIDR_EL2.MECIDWidthm1 + 1 or by other system components, whichever is lower) |
|
An unknown error occurred whilst processing the command, FEAT_MEC is not present in hardware or the SMC is not present if the version is < 0.8. |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.3.2.9. RMM_IDE_KEY_PROG command
Set the key/IV info at Root port for an IDE stream as part of Device Assignment flow. This command is available from v0.6 of the RMM-EL3 interface.
Please refer to IDE-KM RFC for description of the IDE setup sequence and how this will be invoked by RMM.
The key is 256 bits and IV is 96 bits. The caller needs to call this SMC to program this key to the Rx, Tx ports and for each sub-stream corresponding to a single keyset.
4.20.3.2.9.1. FID
0xC40001B7
4.20.3.2.9.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
ecam_address |
x1 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root complex(RC) |
rp_id |
x2 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root port within the root complex(RC) |
Keyset[12]: Dir[11]: Substream[10:8]: StreamID[7:0] |
x3 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
IDE selective stream informationKey set: can be 0 or 1unused bits MBZ. |
KeqQW0 |
x4 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Quad word of key [63:0] |
KeqQW1 |
x5 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Quad word of key [127:64] |
KeqQW2 |
x6 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Quad word of key [191:128] |
KeqQW3 |
x7 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Quad word of key [255:192] |
IFVQW0 |
x8 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Quad word of IV [63:0] |
IFVQW1 |
x9 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Quad word of IV [95:64] |
request_id |
x10 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used only in non-blocking mode. Ignored in blocking mode. |
cookie |
x11 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used only in non-blocking mode. Ignored in blocking mode. |
4.20.3.2.9.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
4.20.3.2.9.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
The Key programming is successful. |
|
The Key programming is not successful. |
|
The Key programming arguments are incorrect. |
|
Unknown error or the SMC is not present if the version is < 0.6. |
|
Returned only for non-blocking mode. IDE-KM interface is busy or request is full. Retry required. |
|
Returned only for non-blocking mode. The caller must issue RMM_IDE_KM_PULL_RESPONSE SMC to pull the response. |
4.20.3.2.10. RMM_IDE_KEY_SET_GO command
Activate the IDE stream at Root Port once the keys have been programmed as part of Device Assignment flow. This command is available from v0.6 of the RMM-EL3 interface.
Please refer to IDE-KM RFC for description of the IDE setup sequence and info on how this will be invoked by RMM.
The caller(RMM) needs to ensure the EL3_IDE_KEY_PROG() call had succeeded prior to this call.
4.20.3.2.10.1. FID
0xC40001B8
4.20.3.2.10.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
ecam_address |
x1 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root complex(RC) |
rp_id |
x2 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root port within the root complex(RC) |
Keyset[12]: Dir[11]: Substream[10:8]: StreamID[7:0] |
x3 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
IDE selective stream information. Key set can be 0 or 1. Unused bits MBZ. |
request_id |
x4 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used only in non-blocking mode. Ignored in blocking mode. |
cookie |
x5 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used only in non-blocking mode. Ignored in blocking mode. |
4.20.3.2.10.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
4.20.3.2.10.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
The Key set go is successful. |
|
The Key set go is not successful. |
|
Incorrect arguments. |
|
Unknown error or the SMC is not present if the version is < 0.6. |
|
Returned only for non-blocking mode. IDE-KM interface is busy or request is full. Retry required. |
|
Returned only for non-blocking mode. The caller must issue RMM_IDE_KM_PULL_RESPONSE SMC to pull the response. |
4.20.3.2.11. RMM_IDE_KEY_SET_STOP command
Deactivate the IDE stream at Root Port as part of Device Assignment flow. This command is available from v0.6 of the RMM-EL3 interface.
Please refer to IDE-KM RFC for description of the IDE setup sequence and info on how this will be invoked by RMM.
This SMC is used to tear down an IDE Stream.
4.20.3.2.11.1. FID
0xC40001B9
4.20.3.2.11.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
ecam_address |
x1 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root complex(RC) |
rp_id |
x2 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root port within the root complex(RC) |
Keyset[12]: Dir[11]: Substream[10:8]: StreamID[7:0] |
x3 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
IDE selective stream information. Key set can be 0 or 1. Unused bits MBZ. |
request_id |
x4 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used only in non-blocking mode. Ignored in blocking mode. |
cookie |
x5 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used only in non-blocking mode. Ignored in blocking mode. |
4.20.3.2.11.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
4.20.3.2.11.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
The Key set stop is successful. |
|
The Key set stop is not successful. |
|
Incorrect arguments. |
|
Unknown error or the SMC is not present if the version is < 0.6. |
|
Returned only for non-blocking mode. IDE-KM interface is busy or request is full. Retry required. |
|
Returned only for non-blocking mode. The caller must issue RMM_IDE_KM_PULL_RESPONSE SMC to pull the response. |
4.20.3.2.12. RMM_IDE_KM_PULL_RESPONSE command
Retrieve the response from Root Port to a previous non-blocking IDE-KM SMC request as part of Device Assignment flow. This command is available from v0.6 of the RMM-EL3 interface.
Please refer to IDE-KM RFC for description of the IDE setup sequence and info on how this will be invoked by RMM.
The response from this call could correspond to any of the last pending requests and the RMM needs to identify the request and populate the response. For blocking calls, this SMC always returns E_RMM_UNK.
4.20.3.2.12.1. FID
0xC40001BA
4.20.3.2.12.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
ecam_address |
x1 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root complex(RC) |
rp_id |
x2 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Used to identify the root port within the root complex(RC) |
4.20.3.2.12.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status |
Result |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Retrieved response corresponding to previous IDE_KM requests. |
Result |
x2 |
[63:0] |
value |
passthrough from requested SMC |
Result |
x3 |
[63:0] |
value |
passthrough from requested SMC |
4.20.3.2.12.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
Response is retrieved successfully. |
|
Arguments to pull response SMC is not correct. |
|
Unknown error or the SMC is not present if the version is < 0.6. |
|
IDE-KM response queue is empty and no response is available. |
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
The previous request was successful. |
|
The previous request was not successful. |
|
Arguments to previous request were incorrect. |
|
Previous request returned unknown error. |
4.20.3.2.13. RMM_RESERVE_MEMORY command
This command is used to reserve memory for the RMM, during RMM boot time. This is not a fully featured dynamic memory allocator, since reservations cannot be freed again, and they must happen during the cold/warm boot phase of RMM. However it allows to size data structures in RMM based on runtime decisions, for instance depending on the number of cores or the amount of memory installed. This command is available from v0.7 of the RMM-EL3 interface.
4.20.3.2.13.1. FID
0xC40001BB
4.20.3.2.13.2. Input values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
fid |
x0 |
[63:0] |
UInt64 |
Command FID |
size |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Size |
required size of the memory region, in bytes |
args |
x2 |
[63:56] |
UInt64 |
alignment requirement, in bits. A value of 16 would return a 64 KB aligned base address. |
args |
x2 |
[55:32] |
UInt64 |
reserved |
args |
x2 |
[31:1] |
UInt64 |
flags (reserved) |
args |
x2 |
[0] |
UInt64 |
flags: local CPU: Determines whether the reservation should be taken from a pool close to the calling CPU. |
4.20.3.2.13.3. Output values
Name |
Register |
Field |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Result |
x0 |
[63:0] |
Error Code |
Command return status. |
address |
x1 |
[63:0] |
Address |
Physical address of the reserved memory area. |
4.20.3.2.13.4. Failure conditions
The table below shows all the possible error codes returned in Result upon
a failure. The errors are ordered by condition check.
ID |
Condition |
|---|---|
|
unrecognised flag bit |
|
if the SMC is not present, if interface version is <0.7 |
|
size of region is larger than the available memory |
|
No errors detected |
4.20.4. RMM-EL3 world switch register save restore convention
As part of NS world switch, EL3 is expected to maintain a register context specific to each world and will save and restore the registers appropriately. This section captures the contract between EL3 and RMM on the register set to be saved and restored.
EL3 must maintain a separate register context for the following:
General purpose registers (x0-x30) and
sp_el0,sp_el2stack pointersEL2 system register context for all enabled features by EL3. These include system registers with the
_EL2prefix. The EL2 physical and virtual timer registers must not be included in this.
As part of SMC forwarding between the NS world and Realm world, EL3 allows x0-x7 to be passed as arguments to Realm and x0-x4 to be used for return arguments back to Non Secure. As per SMCCCv1.2, x4 must be preserved if not being used as return argument by the SMC function and it is the responsibility of RMM to preserve this or use this as a return argument. EL3 will always copy x0-x4 from Realm context to NS Context.
- EL3 must save and restore the following as part of world switch:
EL2 system registers with the exception of
zcr_el2register.PAuth key registers (APIA, APIB, APDA, APDB, APGA).
EL3 will not save some registers as mentioned in the below list. It is the responsibility of RMM to ensure that these are appropriately saved if the Realm World makes use of them:
FP/SIMD registers
SVE registers
SME registers
EL1/0 registers with the exception of PAuth key registers as mentioned above.
zcr_el2 register.
It is essential that EL3 honors this contract to maintain the Confidentiality and integrity of the Realm world.
SMCCC v1.3 allows NS world to specify whether SVE context is in use. In this case, RMM could choose to not save the incoming SVE context but must ensure to clear SVE registers if they have been used in Realm World. The same applies to SME registers.
4.20.5. Types
4.20.5.1. RMM-EL3 Boot Manifest structure
The RMM-EL3 Boot Manifest v0.5 structure contains platform boot information passed from EL3 to RMM. The size of the Boot Manifest is 160 bytes.
The members of the RMM-EL3 Boot Manifest structure are shown in the following table:
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
version |
0 |
uint32_t |
Boot Manifest version |
padding |
4 |
uint32_t |
Reserved, set to 0 |
plat_data |
8 |
uint64_t |
Pointer to Platform Data section |
plat_dram |
16 |
memory_info |
NS DRAM Layout Info structure |
plat_console |
40 |
console_list |
List of consoles available to RMM |
plat_ncoh_region |
64 |
memory_info |
Device non-coherent ranges Info structure |
plat_coh_region |
88 |
memory_info |
Device coherent ranges Info structure |
plat_smmu |
112 |
smmu_list |
List of SMMUs available to RMM (from Boot Manifest v0.5) |
plat_root_complex |
136 |
root_complex_list |
List of PCIe root complexes available to RMM (from Boot Manifest v0.5) |
4.20.5.2. Memory Info structure
Memory Info structure contains information about platform memory layout. The members of this structure are shown in the table below:
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
num_banks |
0 |
uint64_t |
Number of memory banks/device regions |
banks |
8 |
memory_bank * |
Pointer to ‘memory_bank’[] array |
checksum |
16 |
uint64_t |
Checksum |
Checksum is calculated as two’s complement sum of ‘num_banks’, ‘banks’ pointer and memory banks data array pointed by it.
4.20.5.3. Memory Bank/Device region structure
Memory Bank structure contains information about each memory bank/device region:
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
base |
0 |
uint64_t |
Base address |
size |
8 |
uint64_t |
Size of memory bank/device region in bytes |
4.20.5.4. Console List structure
Console List structure contains information about the available consoles for RMM. The members of this structure are shown in the table below:
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
num_consoles |
0 |
uint64_t |
Number of consoles |
consoles |
8 |
console_info * |
Pointer to ‘console_info’[] array |
checksum |
16 |
uint64_t |
Checksum |
Checksum is calculated as two’s complement sum of ‘num_consoles’, ‘consoles’ pointer and the consoles array pointed by it.
4.20.5.5. Console Info structure
Console Info structure contains information about each Console available to RMM.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
base |
0 |
uint64_t |
Console Base address |
map_pages |
8 |
uint64_t |
Num of pages to map for console MMIO |
name |
16 |
char[8] |
Name of console |
clk_in_hz |
24 |
uint64_t |
UART clock (in Hz) for console |
baud_rate |
32 |
uint64_t |
Baud rate |
flags |
40 |
uint64_t |
Additional flags (RES0) |
4.20.5.6. SMMU List structure
SMMU List structure contains information about SMMUs available for RMM. The members of this structure are shown in the table below:
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
num_smmus |
0 |
uint64_t |
Number of SMMUs |
smmus |
8 |
smmu_info * |
Pointer to ‘smmu_info’[] array |
checksum |
16 |
uint64_t |
Checksum |
4.20.5.7. SMMU Info structure
SMMU Info structure contains information about each SMMU available to RMM.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
smmu_base |
0 |
uint64_t |
SMMU Base address |
smmu_r_base |
8 |
uint64_t |
SMMU Realm Pages base address |
4.20.5.8. Root Complex List structure
Root Complex List structure contains information about PCIe root complexes available for RMM. The members of this structure are shown in the table below.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
num_root_complex |
0 |
uint64_t |
Number of root complexes |
rc_info_version |
8 |
uint32_t |
Root Complex Info structure version |
padding |
12 |
uint32_t |
Reserved, set to 0 |
root_complex |
16 |
root_complex_info * |
Pointer to ‘root_complex’[] array |
checksum |
24 |
uint64_t |
Checksum |
The checksum calculation of Root Complex List structure includes all data structures referenced by ‘root_complex_info’ pointer.
4.20.5.9. Root Complex Info structure
Root Complex Info structure contains information about each PCIe root complex available to RMM. The table below describes the members of this structure as per v0.1.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ecam_base |
0 |
uint64_t |
PCIe ECAM Base address |
segment |
8 |
uint8_t |
PCIe segment identifier |
padding[3] |
9 |
uint8_t |
Reserved, set to 0 |
num_root_ports |
12 |
uint32_t |
Number of root ports |
root_ports |
16 |
root_port_info * |
Pointer to ‘root_port_info’[] array |
The Root Complex Info structure version uses the same numbering scheme as described in RMM-EL3 Interface versioning.
4.20.5.10. Root Port Info structure
Root Complex Info structure contains information about each root port in PCIe root complex.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
root_port_id |
0 |
uint16_t |
Root Port identifier |
padding |
2 |
uint16_t |
Reserved, set to 0 |
num_bdf_mappings |
4 |
uint32_t |
Number of BDF mappings |
bdf_mappings |
8 |
bdf_mapping_info * |
Pointer to ‘bdf_mapping_info’[] array |
4.20.5.11. BDF Mapping Info structure
BDF Mapping Info structure contains information about each Device-Bus-Function (BDF) mapping for PCIe root port.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
mapping_base |
0 |
uint16_t |
Base of BDF mapping (inclusive) |
mapping_top |
2 |
uint16_t |
Top of BDF mapping (exclusive) |
mapping_off |
4 |
uint16_t |
Mapping offset, as per Arm Base System Architecture: StreamID = RequesterID[N-1:0] + (1<<N)*Constant_B |
smmu_idx |
6 |
uint16_t |
SMMU index in ‘smmu_info’[] array |
4.20.5.12. EL3 Token Sign Request structure
This structure represents a realm attestation token signing request.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
sig_alg_id |
0 |
uint32_t |
Algorithm idenfier for the sign request. - 0x0: ECC SECP384R1 (ECDSA) - Other values reserved |
rec_granule |
8 |
uint64_t |
Identifier used by RMM to associate a signing request to a realm. Must not be interpreted or modified. |
req_ticket |
16 |
uint64_t |
Value used by RMM to associate request and responses. Must not be interpreted or modified. |
hash_alg_id |
24 |
uint32_t |
Hash algorithm for data in hash_buf - 0x1: SHA2-384 - All other values reserved. |
hash_buf |
32 |
uint8_t[] |
TBS (to-be-signed) Hash of length defined by hash algorithm hash_alg_id |
4.20.5.13. EL3 Token Sign Response structure
This structure represents a realm attestation token signing response.
Name |
Offset |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
rec_granule |
0 |
uint64_t |
Identifier used by RMM to associate a signing request to a realm. Must not be interpreted or modified. |
req_ticket |
8 |
uint64_t |
Value used by RMM to associate request and responses. Must not be interpreted or modified. |
sig_len |
16 |
uint16_t |
Length of the signature_buf field |
signature_buf |
18 |
uint8_t[] |
Signature |